Introduction
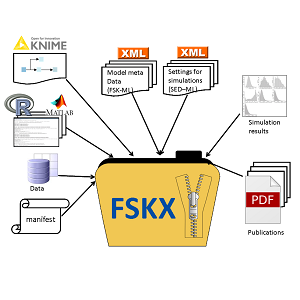
The FAIR Scientific Knowledge eXchange (FSKX) Format is an open, standardized file format designed to facilitate the efficient sharing of scientific models and datasets in a Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, and Reusable (FAIR) manner. Originally developed as the Food Safety Knowledge Exchange (FSKX) Format within the Risk Assessment Knowledge Integration Platform (RAKIP) Initiative, FSKX has evolved into a general-purpose format for exchanging models across multiple scientific domains, including Life Sciences, Food Safety, One Health, and Artificial Intelligence (AI).
This format is particularly relevant in fields where predictive modeling, data simulation, and risk assessment are essential. Unlike other model exchange formats, such as SBML (Systems Biology Markup Language), FSKX retains the original script in its native language (e.g., R, Python, MATLAB) along with metadata and dependencies, ensuring reproducibility without re-implementation.
For further details, refer to the FSKX format specification in the guidance document and its supplementary document, as well as the SWOT analysis publication on FSKX.
Key Benefits of FSKX
1. Native Script Preservation
- Unlike formats such as SBML, which focus on model description and require conversion for execution, FSKX retains models in their original script language (e.g., R, Python, MATLAB) along with execution details, enabling direct use without re-implementation.
2. Comprehensive Metadata Integration
- FSKX includes comprehensive metadata integration by capturing all relevant metadata, input parameters, dependencies, and visualization scripts, enhancing model transparency, understanding, validation, and reuse.
3. Structured Integration of Joined Models
- FSKX enables the storage of joined models and their simulation settings, allowing structured integration where the output of one model serves as the input for another, facilitating complex multi-step simulations through compatible tools (Check out the Tools Utilizing the FSKX Format section below for further information).
4. Cross-Disciplinary Applicability
- Initially focused on food safety and microbiological risk assessment, the format is now being expanded into domains like One Health, toxicology, epidemiology, and AI-driven modeling.
5. Machine Readability and Controlled Vocabularies
- FSKX supports the use of controlled vocabularies to define standardized terminologies, ensuring interoperability across systems, reducing ambiguity in metadata interpretation.
- The RAKIP Harmonization Resources (RAKIP Harmonization Resources) provide a collection of ontology-driven metadata standards, enhancing consistency across models and enabling semantic search and retrieval of models.
Tools Utilizing the FSKX Format
FSK-Lab (KNIME Extension)
Food Safety Knowledge (FSK)-Lab is a graphical workflow-based tool that enables users to generate, read, and execute FSKX compliant models.
Additionally, it allows for joining multiple models where output parameters of one model serve as input parameters for another.
RAKIP-Web Model Repository
The RAKIP-Web Model Repository is a centralized repository providing users with access to FSKX compliant models, their metadata, and online execution capabilities.
Explore RAKIP-Web Model Repository
AI-Driven Web App for FSKX Model Creation (Upcoming)
A new web application is under development that utilizes Large Language Models (LLMs) to assist scientists in automatically extracting metadata and parameters from their models, reducing manual effort.
Future Development and Research Directions
A recent SWOT analysis identified key areas for the strategic development of FSKX, revealing challenges that are now being actively addressed:
- Simplifying Data-to-FSKX Conversion: Transforming scientific data into FSKX models remains complex. To address this, an AI-driven web application is being built, guiding scientists through the conversion process to make FSKX adoption more intuitive and accessible.
- Reducing Annotation Complexity: Extensive metadata annotation was found to be time-consuming, discouraging broader adoption. To address this, an essential variant, eFSKX (essential FSKX), is being developed, offering a streamlined format while preserving core functionalities.
- Automating Metadata Generation: Manually curating metadata is a major barrier for model sharing. In response, AI-driven metadata extraction tools are being created to simplify this process, reducing effort and ensuring consistency.
- Enhancing Model Execution & Accessibility: The dependence on specific software environments limits usability. To solve this, cloud-based execution tools are under development, allowing users to run FSKX models directly in a web environment without requiring local setup.
Get Involved with FSKX
Researchers, developers, and policymakers are encouraged to explore, adopt, and contribute to the FSKX initiative to further drive innovation and collaboration in scientific modeling.
For more information, visit the RAKIP Initiative.
Tutorials
To help you get started and make the most of the FSKX format and the related FSK-Lab KNIME extension, we offer a range of in-depth video and written tutorials that guide you through everything from basic setup to advanced applications. Explore these resources to learn how to integrate, share, and utilize food safety models efficiently, and discover best practices for using the FSKX format.