This manual gives an instruction how to join FSKX compliant models online. This web-service allows to graphically join up to four different FSKX model files into a single combined model. The combined model can then be edited, executed and downloaded.
Concept of joining models
The unique feature of FSK-Web and FSK-Lab is the possibility to join FSKX compliant models in a graphical way in order to generate new models. The FSK-Lab node “FSK Joiner” is the central tool for all model joining services provided in FSK-Web. With the possibility to join models graphically, FSK-Web and FSK-Lab open up the possibility to modularize existing complex or “monolithic” models. Moreover, if the original model already consists of a series of sub-models, each sub-model could become an independent FSKX model.
Note: the FSK Joiner GUI cannot decide whether model joining makes sense scientifically or technically. The user must make sure, that e.g. joined parameters are compatible with respect to their meaning, data type, unit etc. To overcome frequent incompatibility issues between model parameters the FSK Joiner GUI gives the user the opportunity to enter a small “conversion code” to modify the values of a selected parameter before it is assigned to an input of a different model.
1
After login to the FSK-Web Protected Area you will have access to the service for joining and executing FSKX compliant models from the model repository online by using the workflow Online_Joining_Of_Models.
Start the workflow by clicking on the Run button.
2
The workflow provides the main view of the FSK-Web model repository. This view shows a tabular collection of the available models. 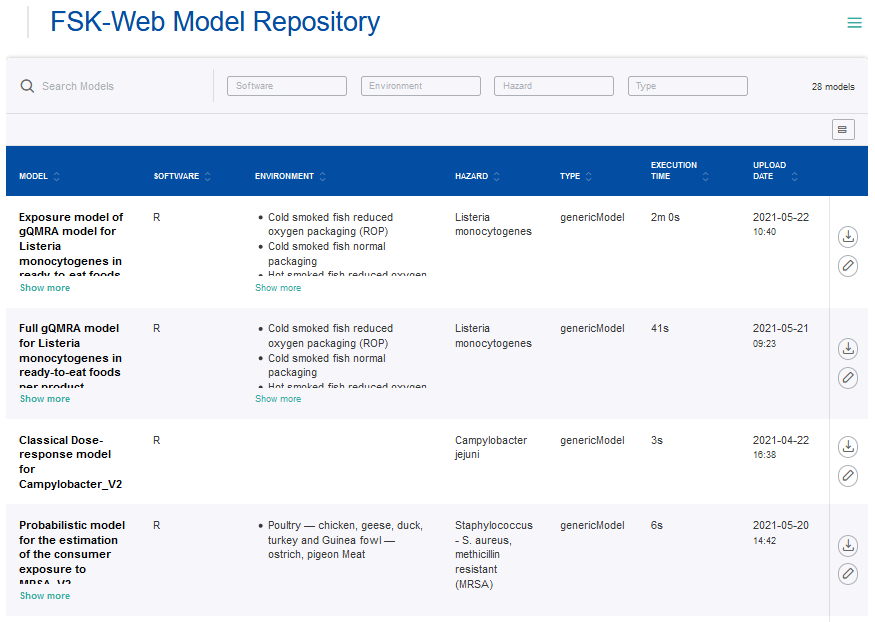
It includes search and filter functionalities for the main model metadata “Software”, “Environment”, “Hazards” and “Type”.
-
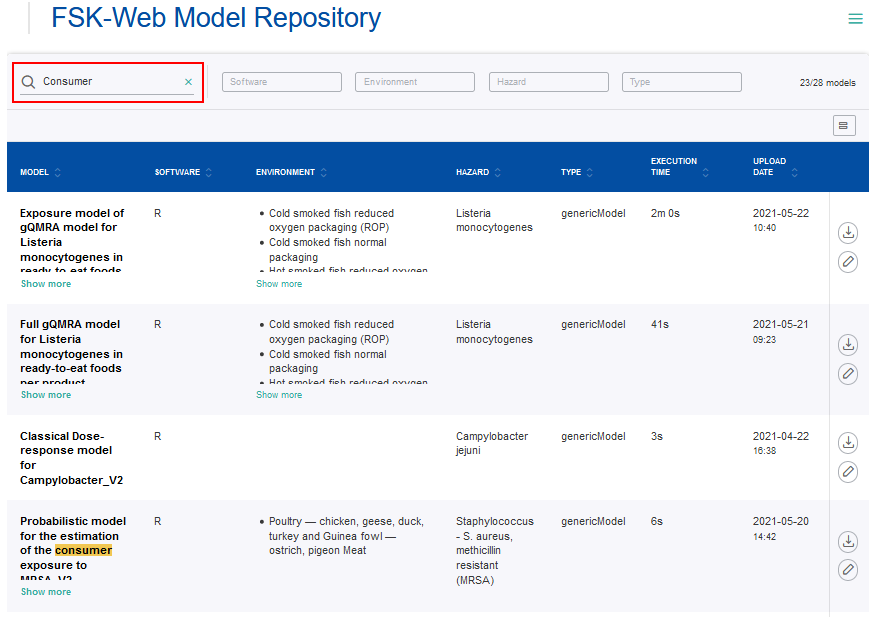
- Entering a keyword into the search box allows filtering over the model metadata
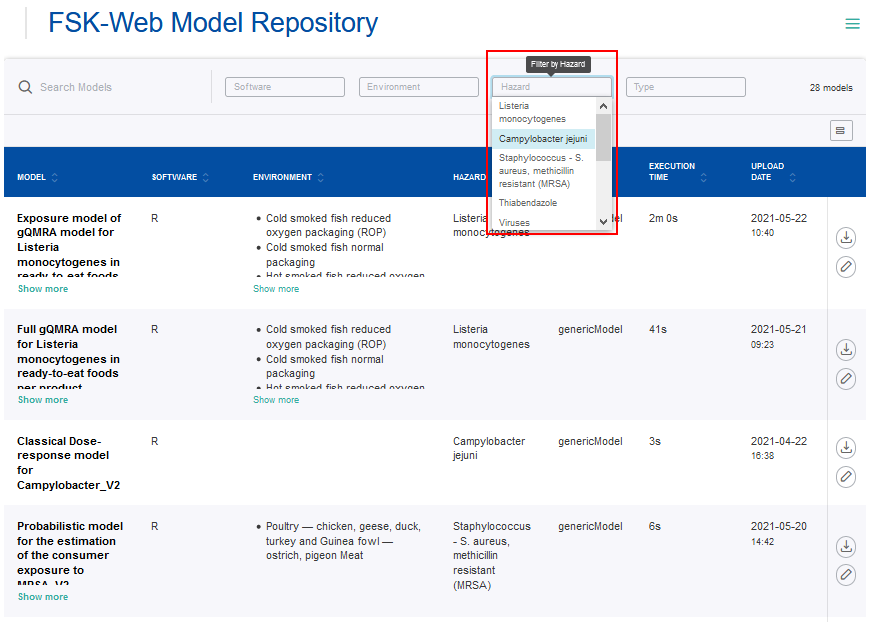
- Clicking on the filters will show the entries available for selection
- Entering a keyword into the search box allows filtering over the model metadata
The FSKX files of models can be downloaded via the Download button and saved to a local device.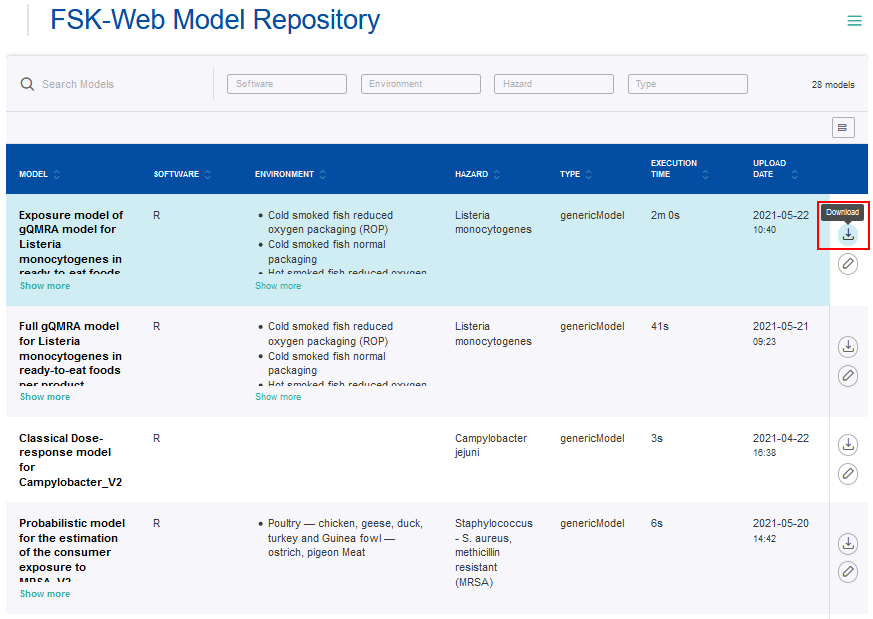
The workflow provides the functionality to join and execute models online. Therefore, models of interest, which should be combined with each other, have to be selected from the table (checkmarks).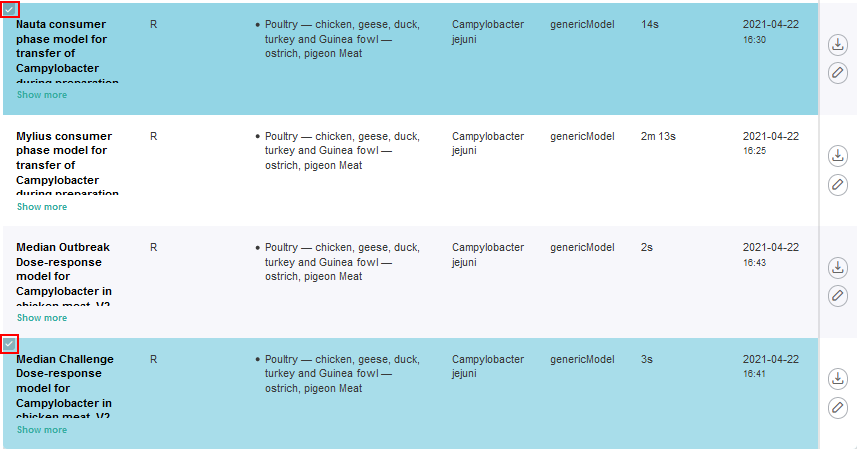
The metadata as well as the model code and resources of the selected models can be reviewed and edited if desired by clicking on the corresponding Edit buttons.
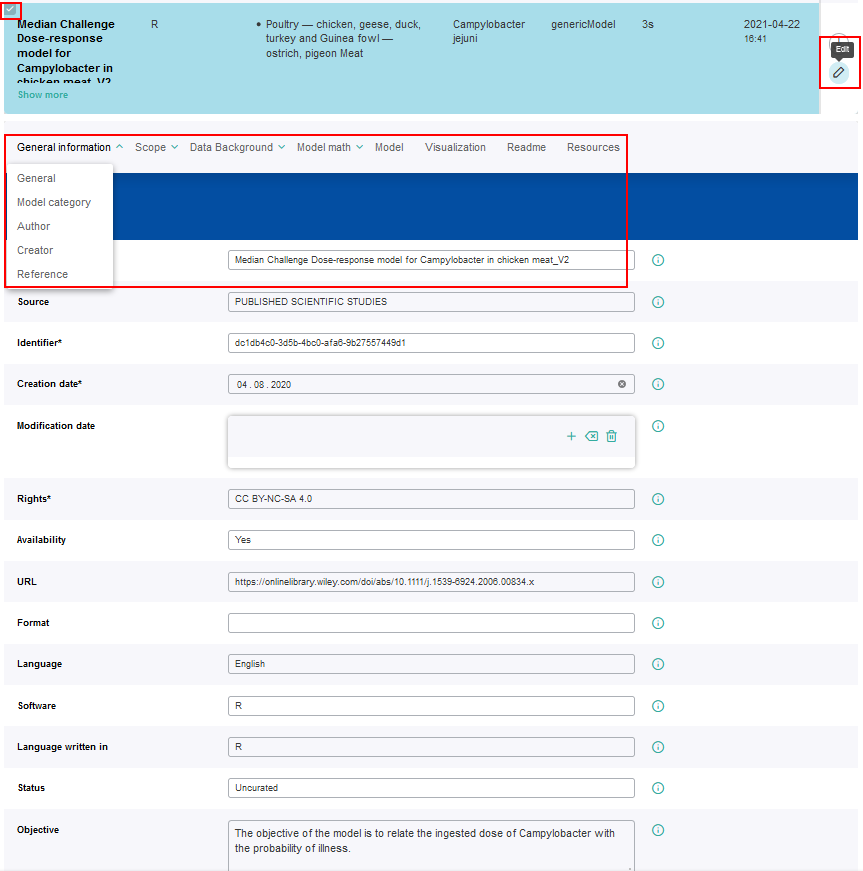
According to the FSKX specifications, the model metadata cover the four main categories “General information”, “Scope”, “Data background” and “Model math”. For each of these main categories the metadata are presented in a structured form via different tabs.
 After selecting the models of interest from the tabular collection (checkmarks), a graphical representation of the models will appear. There the models can be connected with each other by creating links between one or more source parameters of a model with target parameters of other models. Source parameters can be variable and constant input parameters as well as output parameters of a model. Target parameters are only variable input parameters of other models. The variable input parameters are displayed in blue, the constant input parameters in yellow and the output parameters in red. After selecting a source parameter, the possible target parameters will be displayed in green. To support the user in designing connections between parameters, further information of every parameter is displayed when clicking on it.
After selecting the models of interest from the tabular collection (checkmarks), a graphical representation of the models will appear. There the models can be connected with each other by creating links between one or more source parameters of a model with target parameters of other models. Source parameters can be variable and constant input parameters as well as output parameters of a model. Target parameters are only variable input parameters of other models. The variable input parameters are displayed in blue, the constant input parameters in yellow and the output parameters in red. After selecting a source parameter, the possible target parameters will be displayed in green. To support the user in designing connections between parameters, further information of every parameter is displayed when clicking on it. 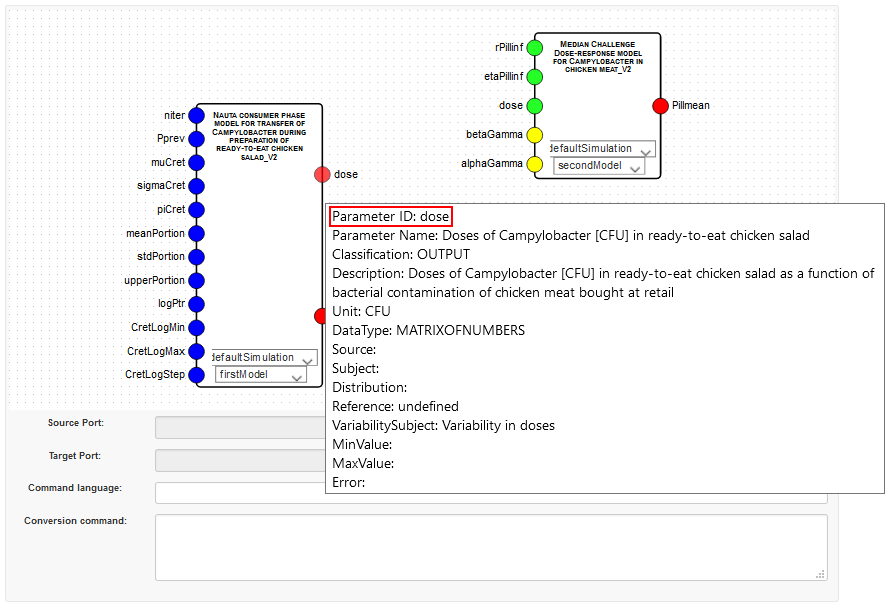
If two parameters should be combined that are not compatible to each other regarding data type or unit for example, there is the opportunity to enter a command in the corresponding field (Conversion command) in order to convert the value of the source parameter to fit the constraints of the target parameter.
Furthermore, there is the option to choose one predefined simulation per model or all available simulations at once that should be carried over to the combined model.
After defining the settings for joining of the models the Next button should be clicked.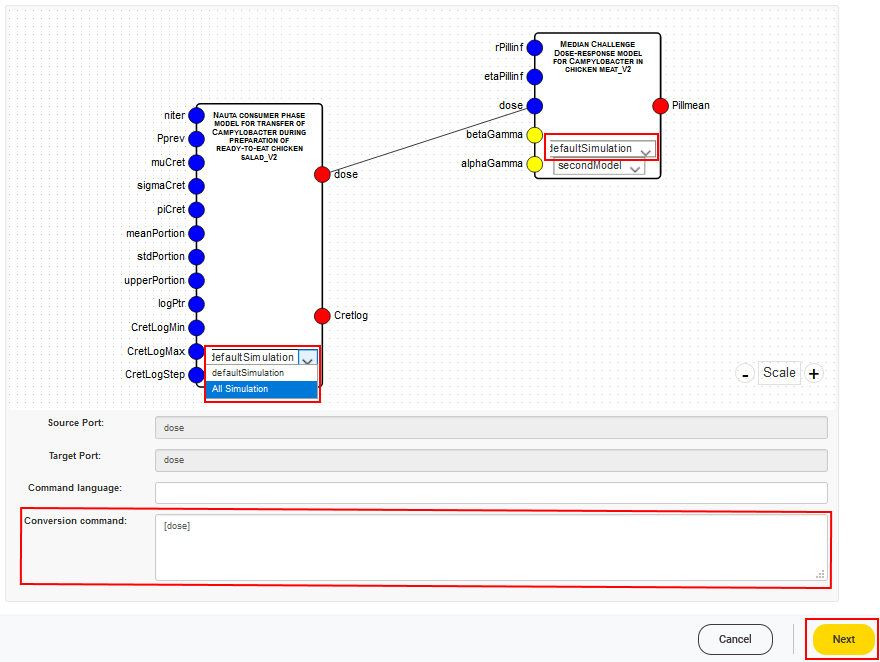
3
The workflow offers access to the metadata of the combined model, so that they can be modified if desired. All metadata are concatenated within the combined model so that no information of individual models will get lost. Information for every metadata field is displayed when clicking on the corresponding i symbol.
After edition of the combined model the Next button should be clicked.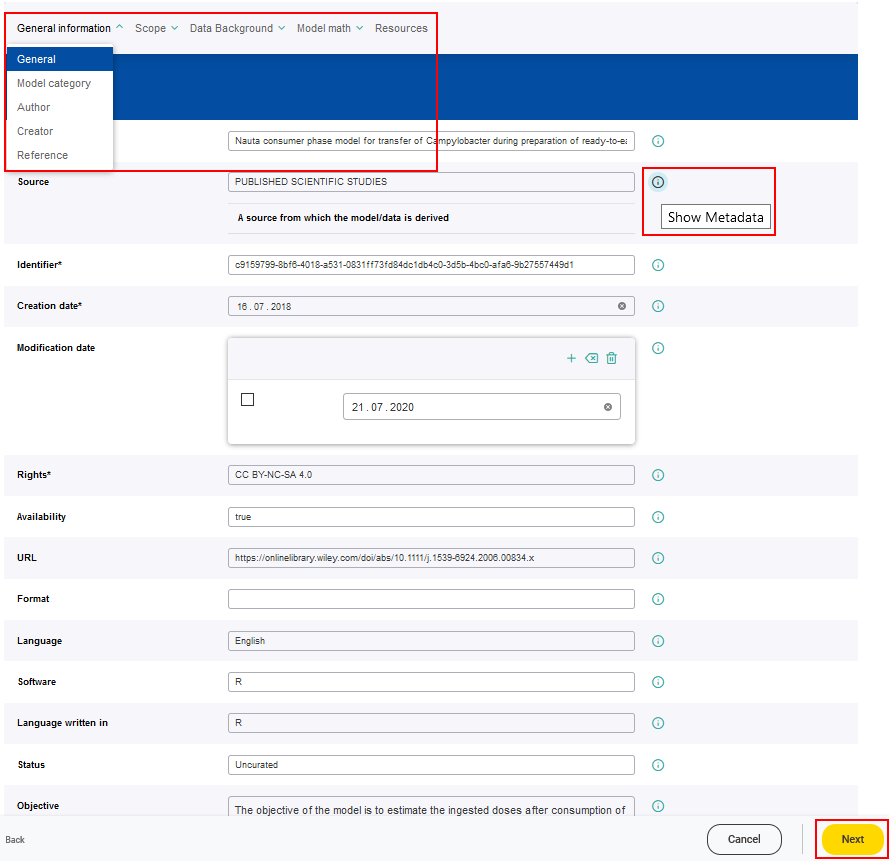
4
The combined model can be executed based on predefined simulation scenarios or user-specific parameter values. It is possible to choose among the available predefined simulations, which were selected in the joiner setting, or to create a new one by modifying the input parameters listed. To support the user in designing a new simulation, further information of every parameter is displayed when clicking on the corresponding i symbol. After joining, the parameters are numbered, indicating to which of the combined models they do belong.
All available predefined simulation can be accessed over the drop-down menu.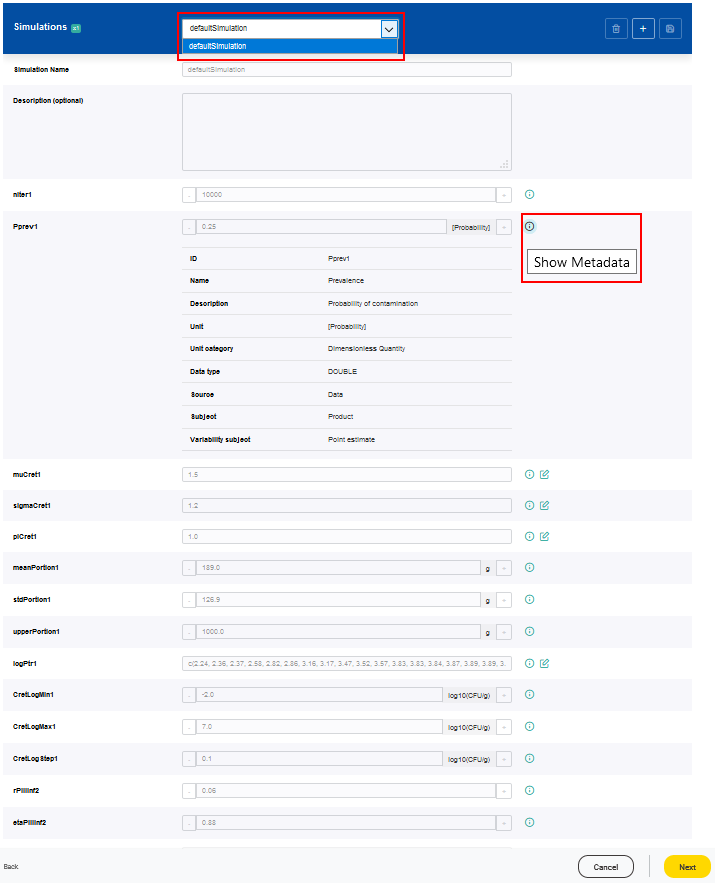
A new simulation setting can be added by clicking on the Add simulation button (plus symbol).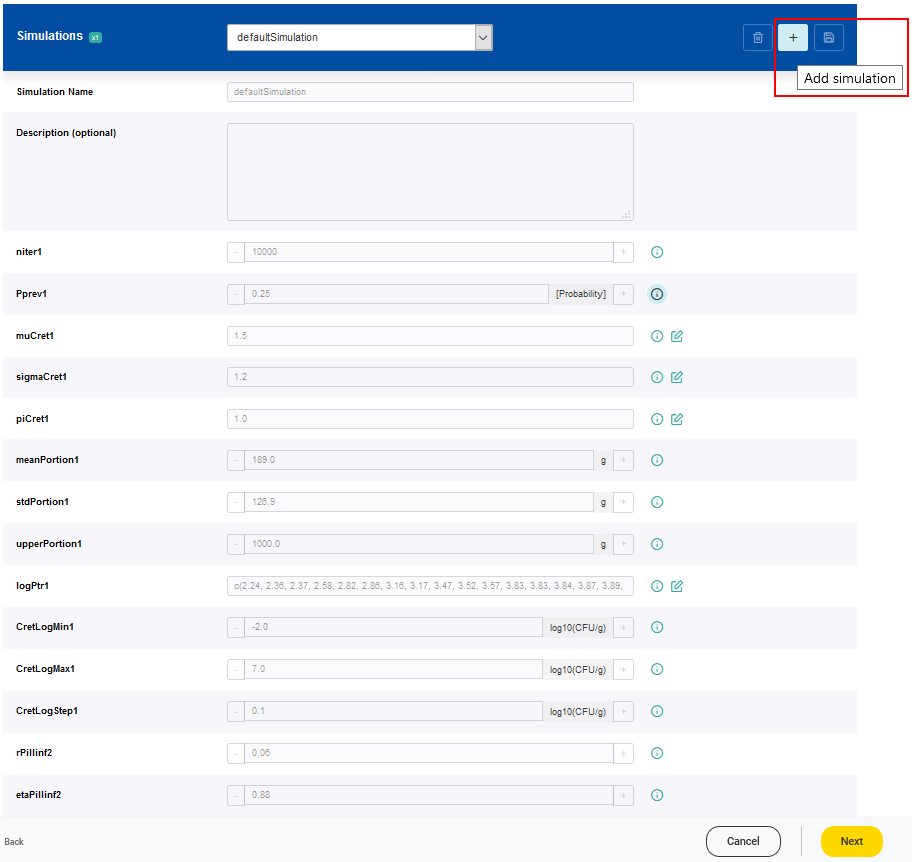
For each new simulation setting a name has to be given. The values of the parameters can be adjusted according to the scenario of interest. It is possible that a range of valid values is predefined for a parameter based on a minimum and a maximum value. Values of parameters which are classified as constant, cannot be modified.
The newly created simulation setting has to be saved by clicking on the Save changes button.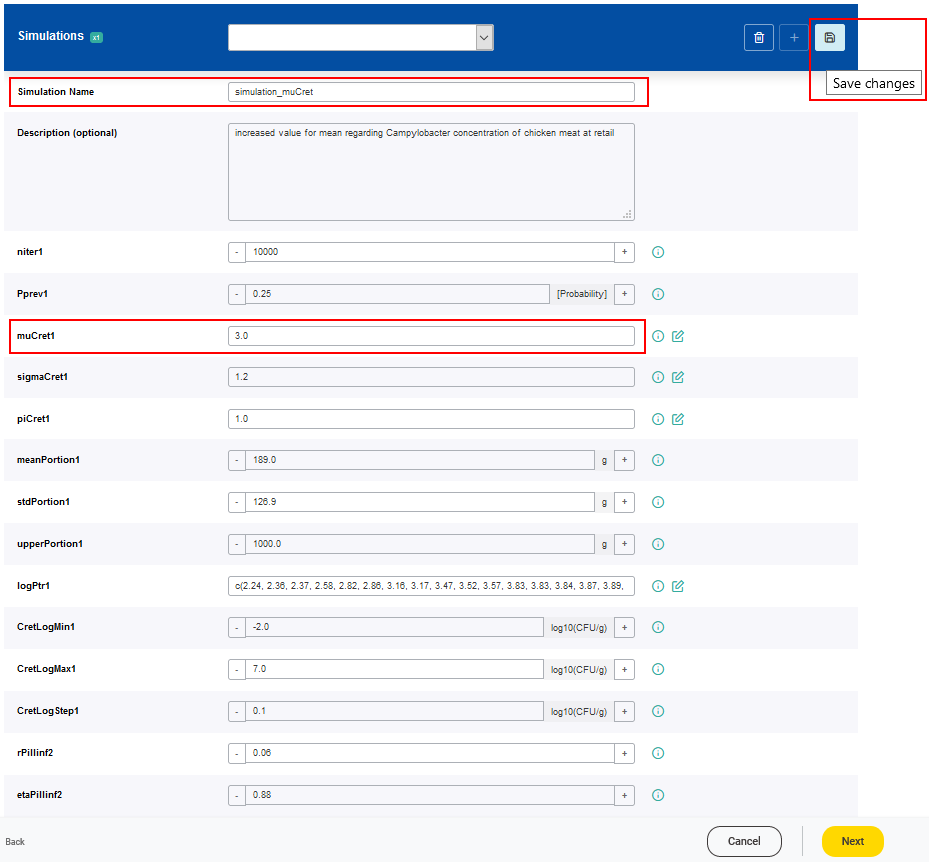
The selected simulation is then executed by clicking on the Next button, meaning each individual model will be executed in order, using generated parameter values from the previous models as input data in accordance with the joining configuration.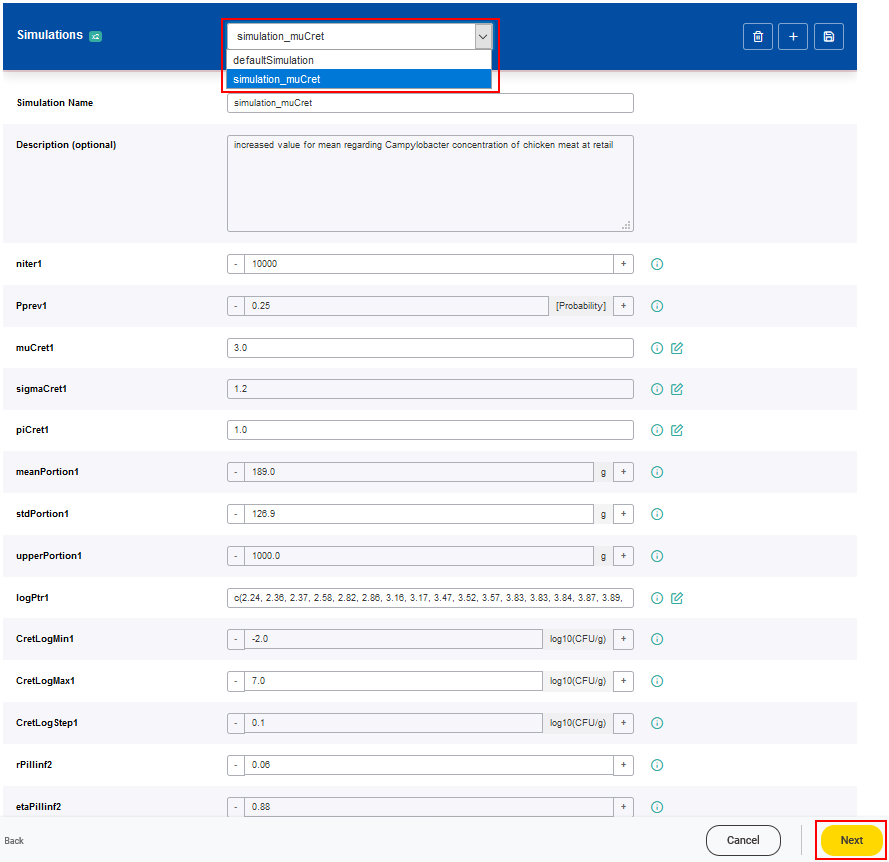
5
The workflow automatically generates a report showing the main settings and the result. The user can download the report (available in different formats .pdf, .docx, and .html) and the combined FSKX model. The embedded figures are the joining diagram based on the joiner setting and the plot of the model result generated by the visualization script of the last joined model. All generated numerical simulation results are included into the downloadable FSKX file (inside the saved R workspace).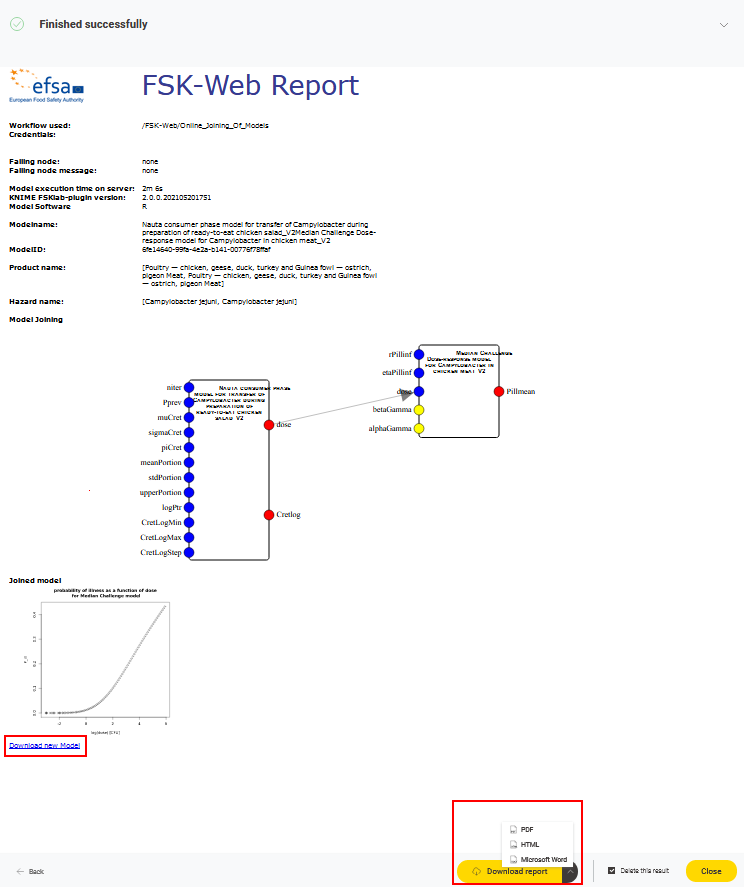
This manual was created with support from EU and EFSA funding (GP/EFSA/AMU/2016/01) by BfR. It only reflects the BfR researchers views. Neither EFSA, EU nor BfR is responsible for any use of the website or the service.EFSA is an agency of the European Union