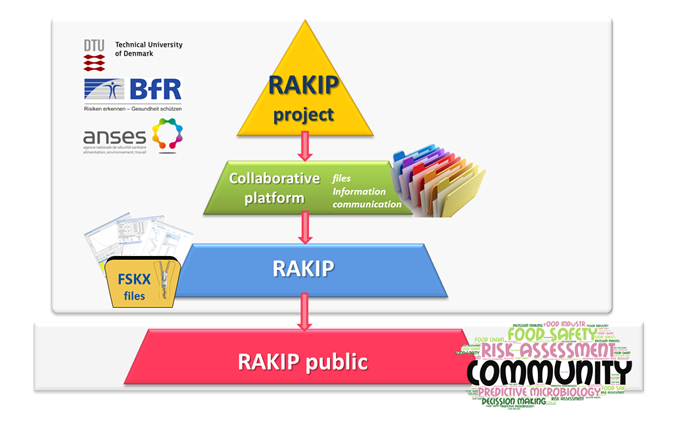
The food safety community is generating a variety of scientific knowledge (e.g. scientific publications, experimental data and mathematical models) and resources (databases and software tools for model generation and application). However, the access to this knowledge and the exchange of information between databases and software tools are currently difficult and time consuming. Therefore, three European institutions specialized in food safety risk assessment (ANSES, BfR and DTU Food as founding members, all members see below) initiated a joint project to establish new community resources facilitating the efficient knowledge integration and exchange into and between IT-based applications and resources. The envisaged “Risk Assessment Modelling and Knowledge Integration Platform” (RAKIP) will be based on harmonized data formats and consistent rules for knowledge annotation. The feasibility of this concept will be exemplified through an RAKIP Web Portal allowing users to access and download risk assessment models, modules thereof and related data in a harmonized file format. These files can then be imported and executed by software tools supporting the proposed harmonized file format. The RAKIP Web Portal therefore also contains supporting resources needed for the harmonized description and exchange of knowledge.
Targeted end users
The RAKIP solutions are designed to support the whole risk assessment community including national and international risk assessment agencies, business operators and academic institutions. Modellers, risk assessors and risk managers will benefit most from the RAKIP portal. However other users like research scientists can also make use of the RAKIP resources, e.g. share their experimental data or apply improved modelling tools in the future.
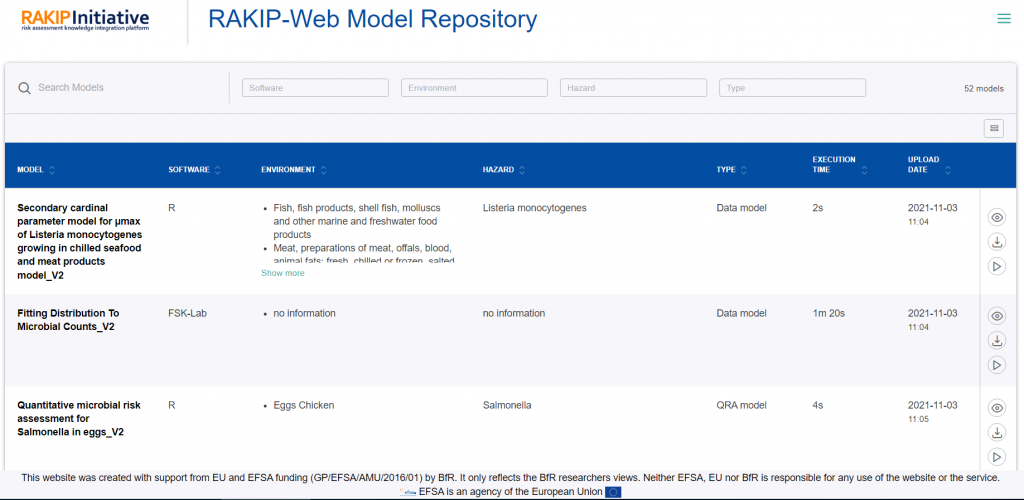
In this sense, the end-users will find in the RAKIP Web Portal a web-based model repository that can be freely assessed and searched, and where models can be shared, searched, downloaded and executed. Modellers can contribute their models to the repository by uploading their models in the harmonized format. The RAKIP Web Portal is however not primarily intended to be a new “press-the-button” model simulation software. It will be improved continuously such that experts and non-experts can make use of it.